STELM: Science, Technology, Engineering (Literacy?!) and Math
STEM activities are unmatched in our virtual Kindergarten class this year. STEM challenges are the perfect storm for beginning conversations, exploring inquiries, answering questions and challenging new ideas. In addition to the academic learning happening through these challenges, students also have opportunities to practice patience, persistence, problem-solving strategies and critical thinking skills while engaging meaningfully within their classroom community.
Recently, I have been on my own exploration. I have been investigating how to purposefully incorporate literacy connections into STEM activities. Here are some of our literacy inspired “STELM” challenges students have worked through:
10 on the Sled – by: Kim Norman, illustrated by: Liza Woodruff
STELM Challenge: Create a sled that can hold ten animals.
Our students were so excited for this challenge. They used materials that they could find around their homes to build a sled and found objects of their choice to represent the ten animals. Students engaged in conversations about the number 10 and how they could group the seats for all the passengers to fit on the sled. In the picture above, the student wrote themselves into the story and shared they would also like to ride on the sled. They shared that now there would be 11 seats because “10+1=11”.
Not a Box – by: Antoinette Portis
STELM Challenge: What can you make your box into?
This one feels like a classic. So simple, but so open-ended and thought provoking. The experience of creating something from “nothing” seems to come so naturally to Kindergarten students. No matter how many groups of students I do this activity with, I am always learning from them. I feel like this challenge gives me a window into student’s imaginations and undoubtedly strengthen’s my view of them as competent and capable learners full of wonder.
The Most Magnificent Thing – by: Ashley Spires
STELM Challenge: What is the most magnificent thing you can make?
Similarly to the challenge of creating something from a box, students thoughts and ideas were not limited to using a box. We did however, challenge them to use recycled materials found at home. Before beginning the process, we listened to the story ‘The Most Magnificent Thing’ by Ashley Spires and asked students to draw a plan before beginning construction. Students entered this activity at their own level. Their plans consisted of pictures, words and symbols to represent their ideas. Not all of their plans matched their finished products – but this was part of the process. The changes and challenges students faced while building their magnificent ‘things’ were a springboard for conversations about different ways to solve problems. One of my favourite moments of learning that happened during this task occurred after I shared my own frustration with my tape that “just would not come off the roll in one piece”. “That’s ok Ms. Turnbull” one of our students shared, “That happened to me once too”, “me too!” other students exclaimed, as we talked about different ways to solve this problem effectively.
The Very Cranky Bear – by: Nick Bland
STELM Challenge: Design a bed for the cranky bear to get some rest in.
We have all experienced the feeling of being tired, cranky, upset or frustrated. So many wonderful conversations of empathy and understanding came from this challenge. Students amazed us with their kind words towards this cranky bear as they constructed cozy beds. They were excited to test out their beds made from LEGO, Play-Doh, blocks and more by using their stuffed animals or dolls. They began acting out the story, snoring and roaring like the bear.
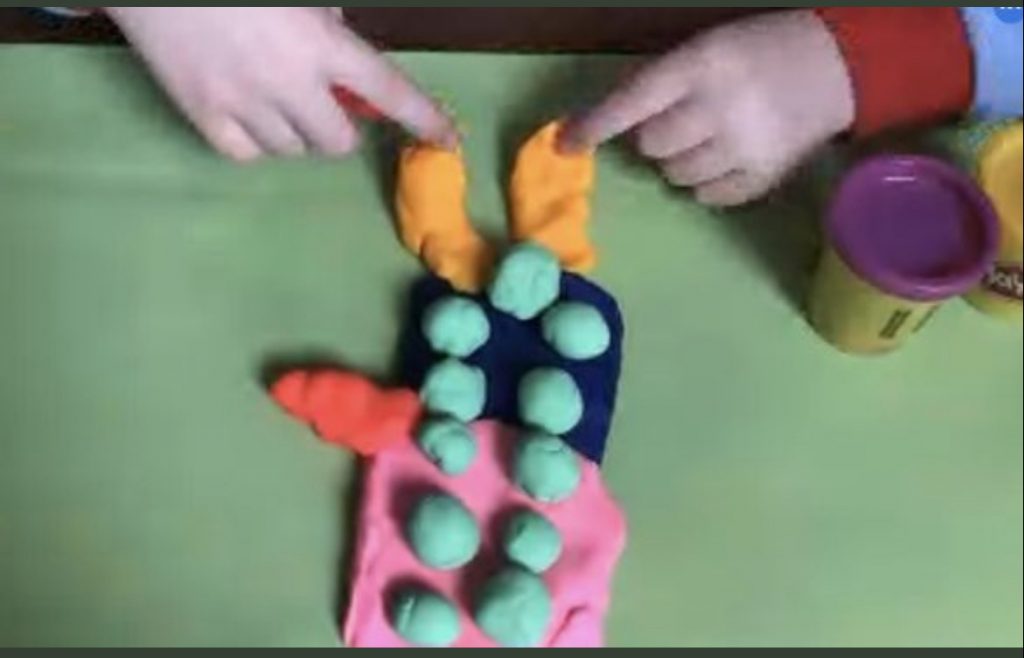
The Mitten – by: Jan Brett
STELM Challenge: How many ‘animals’ can you fit inside a mitten or sock?
The story ‘The Mitten’ by Jan Brett has endless possibilities in regard to follow up activities. For our group of Kindergarten students, we challenged them to think about capacity after listening to this story. We asked them to find something to use as ‘animals’ (with some of the top choices being LEGO or toy animals), and a sock or mitten to put them in. Students explored concepts of counting, spatial sense, and sequencing while they created their own versions of the story.
I am excited to continue thinking about ways to provide my students with meaningful and literacy rich learning opportunities while they engage in hands on experiences that challenge their thinking.
In what ways are literacy experiences imbedded into your STEM activities?
Please note: ETFO’s position on in-person learning remains unchanged. The union firmly believes that the daily, in-person model of instruction and support best meets the educational, developmental and social needs of students, provides the best experience for support, and is the most equitable learning model for all students.
ETFO’s expectation is that elementary virtual learning in any capacity, including through hybrid models of instruction, will end once the pandemic ends.




 https://www.breakoutedu.com/
https://www.breakoutedu.com/