From People for Education, 2019, p. 15
An Individual Education Plan …
- is a working document that is developed and maintained for a student who is deemed exceptional by an Identification, Placement, and Review Committee (IPRC)
- must be developed with input from the parent(s)/guardian(s) and from the student if he or she is 16 years of age or older
- is developed within 30 days of the placement of an exceptional student in a particular program
- must provide a copy to parent(s)/guardian(s)
- must provide a copy to student 16 years or older
- identifies the student’s specific learning expectations
- outlines how the school will address these expectations through appropriate accommodations, program modifications and/or alternative programs as well as specific instructional and assessment strategies
- includes accommodations (i.e. ways to support the student’s learning) and modifications to learning expectations (i.e. often changes to grade level expectations)
- has students deemed with an exceptionality based on a psychoeducational report
- contains IPRC recommendations when developing or reviewing the student’s IEP
Psychoeducational reports/assessments
- completed by trained educational psychologists
- based on testing and observations
- identifies student’s profiles including their strengths and needs
- suggests accommodations and/or modifications to support learning
- includes supports such as special equipment, technology resources, and educational assistance
- “Psychologists are a vital component of special education support in Ontario. These professionals assess students’ special education needs, design interventions for students, and provide direct support to both students and the staff supporting them (Ontario Psychological Association, 2013).” (People for Education, 2019, p. 15)
- “Northern school boards report the highest percentage of schools (58%) without access to a psychologist – this may be due to the difficulty of traveling to more isolated schools in Ontario’s rural North. According to a 2017 report, the cost associated with travel and housing for specialized staff have contributed to a lack of support for students with special education needs in Northern and isolated First Nations communities (Ontario First Nation Special Education Working Group, 2017).” (People for Education, 2019, p. 15)
Role of Identification, Placement, and Review Committee (IPRC)
- consideration must be given to any recommendations made by the IPRC concerning special education programs and services that may be particularly appropriate for meeting the student’s needs
- includes possible funding to support these recommendations made by the IPRC concerning special education programs and services that may be particularly appropriate for meeting the student’s needs
What if the student has not had a psychoeducational assessment?
- an IEP can be developed for students who have not had a psychoeducational assessment and/or have not been identified with an exceptionality under the Special Education Act
- students may also have an IEP developed when they require accommodations, program modifications and/or alternative programs
- students with special needs, not formally identified with an exceptionality, may receive appropriate special education programs and/or services that will allow them to be able to achieve the grade-level learning expectations
- IEPs can include accommodations and modifications documented in the students’ IEP
- some students require alternative expectations, not specifically related to curriculum, that may outline specific learning needs and strategies
Why is the IPRC process so important?
- IPRCs deem students with an exceptionality based on psychological educational assessments
- IPRCs recommend supports and funding to support students’ learning needs
- approximately 50% of students receiving special education support go through the formal IPRC process based on psychoeducational assessment (Ontario Ministry of Education, 2018b)
- students with IPRC identification have a legal right to special education support (Education Act, 1990)
Has there been an increase in students with IEPs in classrooms?
The Ontario Human Rights Commission 2018 policy stated that schools must accommodate students’ disability needs “whether or not a student with a disability falls within the Ministry’s definition of ‘exceptional pupil,’ and whether or not the student has gone through a formal IPRC process, or has an IEP” (Ontario Human Rights Commission, 2018, p. 13).
“Data from the Ontario Ministry of Education show that, while the proportion of students going through the IPRC process has remained relatively stable since 2006-2007, the proportion of students with IEPs has been steadily increasing” (People for Education, 2019).
In other words, students who are not identified via the IPRC process are increasingly receiving special education support through an IEP. With no exceptionality in place, specific supports are not always forthcoming. These supports could include educational assistants, support personnel, and specialized equipment.
Lack of funding for psychoeducational assessments
People for Education (2019) reported:
- “60% of elementary and 53% of secondary schools report that there are restrictions on the number of students who can be assessed each year”
- “92% of elementary schools and 94% of secondary schools report that students waiting for an assessment are receiving some special education support”
With little or no funding for psychoeducational assessments:
- students are put on waiting lists for assessments, sometimes for many years
- students with the greatest needs are moved to the top of the lists leaving other students waiting longer for assessments
- parents with resources pay out-of-pocket for each private assessments costing up to $4000
- 94% of elementary and 81% of secondary schools reported having students on waiting lists for psychoeducational assessments (People for Education, 2019)
- on average there can be up to 6 elementary students and 4 secondary students on waiting lists for professional assessments in their schools (People for Education, 2019)
Gaps in support – Lack of equity in special education funding
|
Students with psychological assessment |
Students with no psychological assessment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
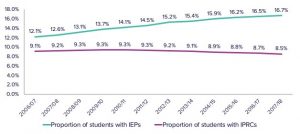
The People for Education have noted an increasing gap between students with IEPs as compared to students with IPRCs (see chart below). This means there are an increasing amount of students with special education needs in classrooms with little or no support as compared to students with special education supports.
|
2017 – 2018 |
16.7% |
8.5% |
|
2016 – 2017 |
16.5% |
8.7% |
|
2015 – 2016 |
16.2% |
8.8% |
|
2014 – 2015 |
15.9% |
8.9% |
|
2013 – 2014 |
15.4% |
9.1% |
|
2012 – 2013 |
15.2% |
9.2% |
| 2011 – 2012 | 14.5% |
9.3% |
|
2010 – 2011 |
14.5% |
9.3% |
It is not Ontario teachers’ imaginations that there are more students with IEPs in their classrooms. With less support for students with IEPs, teachers struggle to meet the needs of these learners and the needs of the rest of the students in their classroom.
“Large class sizes impact the teacher to student ratio. Students with special education needs require greater support and more teacher one-on-one time. Large class sizes make this challenging. Having more special education teachers would help to reduce this challenge by decreasing the teacher to student ratio. Elementary school, Peel DSB” (People for Education, 2019).
Questions about supporting students with special education needs:
- Why are there so many students with IEPs in classrooms without additional adult support?
- What data is being used to develop IEPs without psychoeducational assessments?
- Given the Ontario Human Rights Code, why is the public education system condoning the lack of assess to psychoeducational assessments for students who have less assess to funding?
- Why are teachers solely having to support so many students with IEPs?
- Are Ontario public schools NOT meeting the needs of their most vulnerable students with special education needs?
As an advocate for students with special education needs, I write this blog out of concern for all students with special education needs who are not getting the support they need to learn.
Special Education Teacher,
Collaboratively Yours,
Deb Weston, PhD
References
Education Act, Revised Statutes of Ontario. (1990, c. E.2). Retrieved from the Government of Ontario.
Ontario First Nation Special Education Working Group. (2017). Ontario First Nations Special
Education Review Report. Toronto, ON: Author.
Ontario Human Rights Commission. (2018). Policy: Accessible Education for Students with
Disabilities. Toronto, ON: Author.
Ontario Ministry of Education. (2018a). Education Facts, 2017-2018 (Preliminary). Toronto, ON:
Government of Ontario.
Ontario Ministry of Education. (2018b). 2018-19 Education Funding: A Guide to the Special
Education Grant. Toronto, ON: Queen’s Printer for Ontario.
Ontario Ministry of Education. (2019). Part E: The Individual Education Plan (IEP), Downloaded from http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/policy/os/2017/spec_ed_6.html
Ontario Psychological Association. (2013). Professional Practice Guidelines for School Psychologists in Ontario. Toronto, ON: Author.
People for Education. (2019). Annual report on Ontario’s publically funded schools 2019. People for Education. Downloaded from https://peopleforeducation.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/PFE-2019-Annual-Report.pdf.

In my board we are explicitly told not to request IPRCs unless absolutely necessary or going into a system class – even when the psych assessment recommends it. This means that parents who have no understanding of the system will not IPRC their child even if they would have wanted it as they don’t know what an IPRC is or how to request one. This means that our children are still not receiving consideration for adequate funding.
Thank you for sharing this information. It’s telling that your story is shared by so many teachers and parents across Ontario. This is another reason to push more for support for students with education needs. Deb
I was the special education teacher and MART in my building. I was instructed that all students regardless of identification on IEP would receive support. This year we removed HSP and moved to integration. We just found out that our SNA is being pulled for the building. She has been integral to supporting a class of high needs primarily those with integration. These are students who were not allowed to go through the IPRC process. Who do I contact? Our school had 100 students on IEP many who have identifications on répète but only about 20 with Identifications.