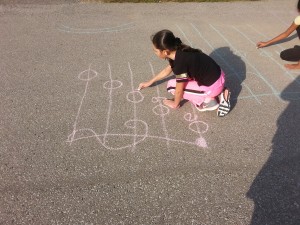The students and I often have a similar struggle when we return to school in September. After a whole summer of biking, running around and enjoying the great outdoors, we come back to school and spend a large portion of 8 hours a day inside. It can make you crave the sunlight, fresh air and make one or two of us a little restless.
To help with the transition, I try to do a few music lessons outdoors in September and October. It is amazing what you can do with instruments and sidewalk chalk.
If you have any kind of concrete outside your building, the possibilities are endless for using chalk instead of a pencil for a period. Early in September, I have my students simply start by drawing any musical symbols that they know. For some students, this requires a bit of prompting or visual cuing but others come up with a plethora of symbols. After doing this simple activity, I can begin to gather information on which students will need support and others who will require challenges when writing and reading music. I also like to go outside to review the musical staff with my junior students. We practice drawing a staff and placing all the notes they know on it. I also draw a giant staff outside and we do relay races to remind us of the placement of the pitches on the staff.
For the younger students, this is the time to let them experiment with a variety of instruments outdoors. The kindergarten and grade one students can make all the noise that they want without making the volume unbearable, as it would be indoors. I encourage my students to create as many sounds as possible with something like a rhythm stick, tambourine or found objects outside. The students begin to realize how to create different timbres of sounds which will come in handy for their future musical journeys.
Before you head for the outdoors, remember to:
Inform the office of where you are going to be. I e-mail my head secretary at the beginning of the week to let her know which classes I will be taking outside.
Take some sort of communication tool with you outside. Either a cell phone or a walkie talkie will work. That way, if a parent unexpectedly shows up to pick up their child, the office is able to reach you.
Finally, inform the classroom teacher of your intentions, so that they can have the students ready with jackets and outdoor shoes.
Overheard in my Ontario Classroom…
The creative process includes the very important element of sharing one’s work. Therefore, my classroom constantly has groups or individuals sharing their creations. In week two of my class, my grade two students had the assignment of sharing a poem using different kinds of voices. As one group of 4 began to recite their poem, one of the boys let out a very large fart. Shockingly, the class and the boys managed to keep it together and finish their poem very successfully. After the class applauded, the boys began to walk back to their seats. As they did, I overheard one boy say to the other: “I wish you would have waited until the end to fart. It would have been a really great finale.”