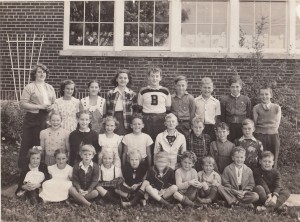I was born into the union. In 1966, my father worked for Tommy Douglas and ran for the an NDP member of parliament in the Ottawa region. Photo below with my father looking over Tommy’s shoulder.

And my mother was on the CUPE (Canadian Union of Public Employees) collective bargaining unit for the secretaries (i.e.typists) local in the early 1970s.
My first experience with collective bargaining (CB) was with my mother. I remember my mother being gone for long periods and coming home very late at night bargaining for CUPE members’ rights. My mother says it took a great deal of work hours and strategy to advocate for members’ pay and working conditions. Every Labour Day, my family marched in the Toronto parade. I got to wear very cool white gloves and wave to people! I also remember walking picket lines with my mother.
At the time of my mother’s involvement in CUPE’s collective bargaining, she had four children, aged 11 (me), 9, 3, and 1 years old. The long hours and family commitments eventually led to her leaving for another role. My mother ultimately became a teacher and teacher union steward.
When I started teaching, I had a ready-made union mentor (even though she was part OSSFT – Ontario Secondary School Teachers Federation). I was fortunate to have my mother to walk me through the importance and processes of collective bargaining and collective agreements. When talking to new teachers, I often wonder how much they know about collective bargaining and the importance of collective agreements.
Fortunately, I have attended two ETFO collective bargaining professional development sessions and have learned specifically about ETFOs collective bargaining processes.
Until these PD sessions, I felt safe in my practice as a teacher and as an ETFO member. But, in the PD sessions, I also heard stories that have made me feel distressed by what EFTO members had experienced in their schools. These stories and the calibre of members involved in ETFO collective bargaining has implored me into posting a blog for new members.
In my last collective bargaining PD session, Heather Ann McConnell , a labour lawyer with Goldblatt Partners, spoke eloquently about collective bargaining, the collective agreement, and ETFO member rights. I asked her what new ETFO members needed to know about collective bargaining. She listed the following points:
- Understand the process and terms of collective bargaining
- Understand member rights as an ETFO member
- Understand the separate bargaining units within ETFO
- Attend PD seminars on collective bargaining
- Talk to ETFO stewards
- Get involved by attending local and provincial annual general meetings
- Develop ETFO leadership at school, local, and provincial levels
What really hit me was when Heather stated:
“ the most important issue in collective bargaining is that collective agreements need to be reinforced to be worth the paper they are written upon” or in other words, “use it or lose it”.
Did you know that …
- In the years of the one room school house, teachers were obligated to teach students, clean classrooms, chop wood for the fire, prime the well, and feed the students for poverty level wages.
- At one point, teachers who married or became pregnant had to quit their jobs.
- In 1888, one of the first teacher unions was formed by the Lady Teachers’ Association of Toronto, to fight for better wages and working conditions – just like teachers do today over 130 years later.
- In the 1920s, there were two volunteer teacher organizations, one for women and one for men. The men got paid more BTW.
- In 1944, the first teachers’ federation was established. This lead to more teacher rights, an increase in salary, and a pay grid based on qualifications and experience.
Source: It’s Elementary: A Brief History of Ontario’s Elementary Teachers and Their Federations
My grandmother’s one room classroom near Feversham, Grey County, Ontario (first row, 4th from the left).

My mother’s classroom in King Township, Ontario (second row, 2nd from the left).
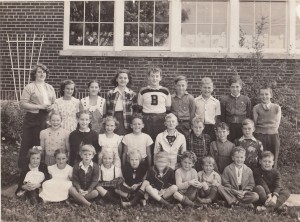
Collective bargaining and the collective agreements that follow are the reason for teachers’ current pay and working conditions.
I’m very pleased that I am not obligated to clean classrooms or to prepared lunches for all my students. I am proud that I get paid based on my level of experience and qualifications, regardless of my gender.
Check out some of the resources below. Learn about your rights. Be part of your union. Make sure your collective agreement is being honoured. Read your collective agreement today!
Collaboratively Yours,
Deb Weston
It’s Elementary: A Brief History of Ontario’s Elementary Teachers and Their Federations

Part I of It’s Elementary: A Brief History of Ontario’s Elementary Teachers and Their Federations
Part III of It’s Elementary: A Brief History of Ontario’s Public Elementary School Teachers and their Federations
Kitchen, J., & Petrarca, D. (2013/2014). Teacher Preparation in Ontario: A History, Journal of Teaching & Learning, Brock University, 8(1), 56-71
The Importance of Collective Agreements: Protecting Salary and Working Conditions
This resource discusses salary, insured benefits, sick leave entitlement, teachers’ work days, teachers’ job allocation, and protection against arbitrary discipline. It discussed how collective bargaining is on ongoing process which, over time, evolves to achieve more protection and better working conditions for teachers. The role of collective bargaining is to fill in gaps in existing law and to be flexible enough to respond to changing conditions in education. This means that each collective agreement has a deep history of hard won rights and working conditions. Every ETFO member has ownership to their collective agreement.
Source: The Importance of Collective Agreements: Protecting Salary and Working Conditions
From ETFOs: Defending Working & Learning Conditions
“Each and every ETFO member has a stake in reading and understanding the agreement, and in supporting the local bargaining process. Your principal, superintendents, and trustees may be well-intentioned individuals committed to helping you do your job. But good intentions are no substitute for the negotiated, legally-enforceable document that unambiguously sets forth your rights in the workplace. In short, collective bargaining protects your rights as an education worker. Read your collective agreement today.”


 the terms we were going to be investigating, students were asked to look at some of his works and identify the geometric concepts contained within. They were amazed by the number of concepts that could be found in his works. They measured angles and classified them as acute, right or obtuse. They compared shapes and lines, some even realizing that some of the shapes were created by other shapes and lines intersecting.
the terms we were going to be investigating, students were asked to look at some of his works and identify the geometric concepts contained within. They were amazed by the number of concepts that could be found in his works. They measured angles and classified them as acute, right or obtuse. They compared shapes and lines, some even realizing that some of the shapes were created by other shapes and lines intersecting. Once we had the chance to investigate Kandinsky’s works, we set off on a mission to try to create our own Kandinsky inspired works using Google Drawings. In pairs, students used at least 7 of the concepts that we were learning about to create abstract, labeled digital drawings.
Once we had the chance to investigate Kandinsky’s works, we set off on a mission to try to create our own Kandinsky inspired works using Google Drawings. In pairs, students used at least 7 of the concepts that we were learning about to create abstract, labeled digital drawings.