A few years ago when I started hearing about teachers doing coding and robotics in the classroom I dismissed it as a fad. I didn’t understand the value of coding nor could I see how it tied to the curriculum. However, I recognize as a professional learner my initial reaction to something radically new can sometimes be resistance. I think that this is because I can’t see myself fitting “one more thing” into my classroom practice. I always have to give myself time to process, research, find the value and then finally accept it. After I have tried a new practice with students and see the beneficial outcomes, I endorse it and then begin to share it widely with colleagues.
When I began the journey with coding and looked at code.org I tried it on my own and admittedly, understood very little. I went to more workshops and conferences but avoided the coding and robotics thinking that it just wasn’t my bag. Then I had a colleague that dragged me in to the world of coding and robotics. We worked together. I’ve since become convinced that we need to teach all students how to code. I have also figured out that you don’t need any robots to do it. In fact, when you start-you don’t even need a computer.
The above picture is a coding game that I used recently with a grade one and two class. Students placed their obstacles (rocks) on a grid. They placed their “gemstone” or finish on a spot on the board and their “robot” (animal) on another spot. They wrote their code on a sticky note using arrows and then had their partner take their robot through the code to test it for “bugs”. A big part of coding is knowing your left from your right and being able to write instructions that someone else can follow. We started out the day coding one another to walk in a square using only: “forward” “turn left” and “turn right”. It was amazing to see how much problem solving took place. They were using positional language, procedural writing, clear communication, visualization and proportional reasoning. Their thinking was exploding! The students were engaged in the learning and well on their way to being able to code something online. From there we explored the Scratch Jr. app. After a short look together at what the different “buttons/blocks” meant they were able to code independently. As teachers we sometimes get bogged down in the fact that we don’t have the money to purchase the technology and shy away from trying things based on the fact that we don’t have “the stuff”. However, laying the groundwork before introducing the technology piece to students is key. We need to always consider the pedagogy before the technology.













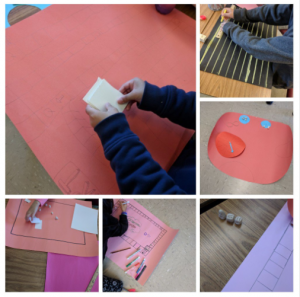 As I mentioned before, we are well into the creation stage and will continue in the new year. I do wonder however, if by calling it a board game, if I have steered them into a specific direction. Could it have been just a game where I may have seen a greater diversity of materials being used from physical to online? Did I in reality just do the very thing that bothered me so much about my mother’s course? Ask students to create something that wasn’t bored and yet steered them all into asking for bristol board? I’m on a path to really reflect on the types of tasks that I design for students while expecting them to become critical thinkers who are creative. This has now become food for thought for future tasks that we’ll embark on. Please stay tuned!
As I mentioned before, we are well into the creation stage and will continue in the new year. I do wonder however, if by calling it a board game, if I have steered them into a specific direction. Could it have been just a game where I may have seen a greater diversity of materials being used from physical to online? Did I in reality just do the very thing that bothered me so much about my mother’s course? Ask students to create something that wasn’t bored and yet steered them all into asking for bristol board? I’m on a path to really reflect on the types of tasks that I design for students while expecting them to become critical thinkers who are creative. This has now become food for thought for future tasks that we’ll embark on. Please stay tuned!