This year, as in times past, planning my math program was filled with the usual excitement of clustering expectations and imagining ways in which I could creatively address the curriculum. Teaching a grade 3/4 combined grade for the first time, I was eager to be on top of my planning and ensure that I was creating parallel learning experiences by simultaneously addressing the curriculum expectations for both grades.

When planning the learning experiences, I colour code the strands, cut out each expectation and cluster them according to big ideas. This results in cross-strand learning experiences.
For my first series of learning experiences, I really wanted to invite my scholars to engage with number lines as a model that would help to make their thinking visible, but also as a tool for exploring many math concepts such as quantity and measurement. A number line is a line segment that can either be vertical or horizontal that represent a series of numbers that are marked at intervals. Re(introducing) number lines to my scholars early on in the year was important for me because I view number lines as an invaluable math model. Every day numbers lines are used to measure time – a clock; distance – a ruler; capacity – a measuring cup; temperature – a thermometer and mass – a scale. Number lines also allow students to model the strategies they use when adding and subtracting, as well as composing and decomposing numbers. Starting with the exploration of number lines proved to be an important first learning for my grade 3/4 math class.
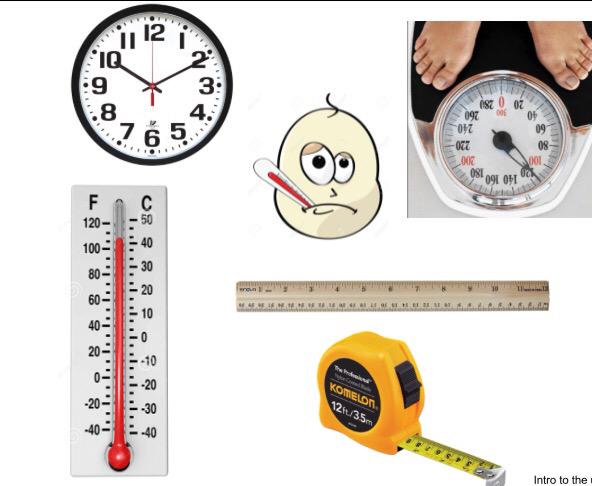

Students were able to identify a variety of tools that have number lines embedded in their function.
Beginning the year this way was exciting but it was even more invigorating when I realized how many authentic, cross-strand connections that actually took place by centring the learning around investigating the use of a simple tool. The following are a few reflections from the journey:
1. Once the orientation of a number line was solidified, scholars were able to make connections between the number line drawn on the board with the number lines embedded in everyday objects.
The most prominent feature in my class at the start of the school year were the quantity number lines hanging from my classroom ceiling. These were made by cutting pool noodles into two-inch disk and placing them on rope. One was counting by twos (two-coloured pool noodles) and grouped by twenties to hang on the ceiling. The other was counting by fives with alternating colours and grouped by 25s. Students were invited to inquire about the quantity of pool noodles, the groupings, the skip counting, etc. and this became the introduction to number lines for the year. Using the quantity number line along with an actual number line that marked the perimeter of the front of my class, we explored the nuances of number lines by describing their directionality of increasing and decreasing quantity. We also explore the ways in which intervals could be marked on an open number line so that users didn’t necessarily have to always count by ones, but skip counting was made possible by using appropriate quantity intervals. We then named all the number lines that were present in the classroom. They noticed the clock on the wall to be a circular number line and the “How Much are Your Growing” height chart as a vertical number line. Excitement bubbled as scholars scrutinized the number lines we named by the elements of number lines that we had previously defined. They were set and ready to continue their investigation of how number lines could truly enhance their learning experiences as young mathematicians.


Quantity number lines hanging from the ceiling of my classroom.
2. Counting on a number line allowed number patterns and relationships to jump out at scholars.
Once scholars were comfortable describing the orientation and use of number lines, we began exploring quantity by representing skip counting on an open number line. We counted forward by tens by modeling jumps of +10 on an open number line and then later by nines. Scholars were able to name the relationships between counting by tens and nines by creating expressions that named the pattern (i.e. 10-1). We then explored counting forward by 100s, 50s, 20, and 11 to explore the other number patterns and relationships. Once scholars we comfortable counting forwards, we then counted backwards. They noticed relationships around place value, odd, and even numbers, what happens when counting by numbers with specific digits, and the nuances of increasing and decreasing values. The grade 4 scholars were then invited to apply their understanding of skip counting by whole numbers and moved deeper into counting by fractional amounts and decimal numbers up to tenths. Students were taught to use the number line to keep track of their thinking by using it as a thinking tool and not a picture. Hence, numbers and jumps were added in sequence as the counting progressed and not merely by drawing the elements of the number line and labelling them afterwards.

Counting forward by 9 using a quantity number line. Student notice and described patterns.
3. Using number lines as a tool for measurement invited scholars to apply their understanding of number concepts.
Measuring mass using a triple balance scale, capacity with graduated cylinders and time with a clock were all the more meaningful when scholars were able to apply their understandings of using number lines as a tool for mathematical thinking. This is how our Number Sense learning experiences married Measurement. When scholars measured mass using the triple balance scales, they applied their understanding of decomposing numbers into place value (including tenths for grade 4s) in order to calculate the mass of the item they were measuring. Similarly, when measuring capacity using a graduated cylinder, scholars needed to apply their understanding of skip counting in order to accurately represent the capacity using a variety of differently shaped and sized graduated cylinders that each increased by differently valued intervals. Given their prior knowledge of skip counting, and composing and decomposing numbers using number line, measurement became a context to continue to expand their understanding of quantity.
4. Counting on a number line open up the way to modelling mental math strategies for addition and subtraction.
Once scholars were comfortable skip counting, composing numbers and measuring different units of measure using number lines, adding and subtracting was a natural next step and application of their previous understanding. Using addition and subtraction strings (intentionally crafted equations to be solved using mental math strategies), I modelled scholars’ mental math strategies visibly on a number line. Scholars articulated strategies such as adding on, counting, back, compensation and even decomposing numbers in order to add and subtract. The application went through the roof when grade 4 scholars were able to demonstrate their understanding of elapsed time using these same strategies. This was especially helpful because scholars could be fluid with the units of time they were adding or subtracting (i.e. hours and minutes) and could avoid the complexities of the base-60 system of time (i.e. 60 seconds in 1 minute, 60 minutes in 1 hour) when it came to calculating time that involved “regrouping” which uses a base-10 number system.
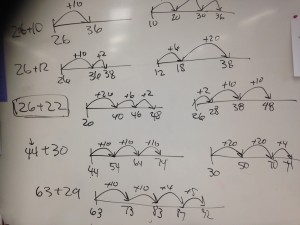
Students articulated mental strategies while I modelled them on an open number line.
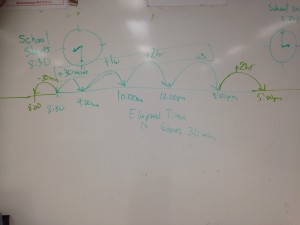
Student calculating elapsed time using strategies for addition and subtraction.
During these first months of school,not only was I able to introduce scholars to an invaluable learning tool, the number line, but I was also able to seamlessly integrate two strands of math and a multiplicity of essential number concepts. The number line has truly been a game changer in my class. I am already seeing the connections for moving forward with experiences that explore data management (scales on a graph) and geometry (side length attributes of polygons). …the journey continues…